The Freedom Solution: Unlocking the Benefits of Captive Insurance
- by Jose Bryant
Captive insurance, a form of self-insurance, has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses seeking to manage their risks while gaining more control over their insurance programs. This unique concept allows companies to create their own insurance company, known as a captive, to provide coverage for their specific needs. By establishing a captive insurance structure, businesses can tailor their policies to meet their exact requirements, resulting in customized coverage and potentially significant cost savings.
One of the most popular types of captive insurance structures is known as a 831(b) captive, named after the section of the Internal Revenue Code that governs its tax treatment. Under the IRS 831(b) tax code, qualifying captives are classified as microcaptives, which enjoy favorable tax advantages. These benefits include the ability to take tax-deductible premiums and potentially tax-exempt investment income up to a certain threshold.
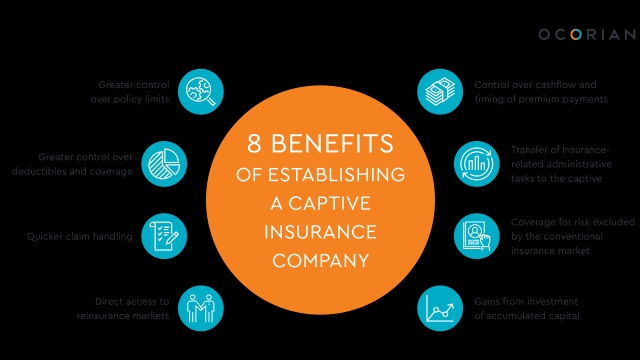
By harnessing the power of a captive insurance structure, companies can unlock a range of benefits. Not only can captives provide coverage for risks that may be otherwise challenging to obtain or prohibitively expensive in the traditional insurance marketplace, but they also offer an opportunity to build wealth by retaining profits within the captive and potentially experiencing tax advantages.
In the following sections, we will explore the intricacies of captive insurance, delve into the unique advantages it offers, and guide you through the process of establishing and maintaining your own captive insurance company. Join us on this journey as we uncover the freedom solution that captive insurance can provide to businesses of all sizes.
Understanding Captive Insurance
Captive insurance is a unique form of self-insurance that offers many benefits for businesses. It allows companies to create their own insurance company to cover risks that are not adequately addressed by the traditional insurance market. With captive insurance, businesses can tailor their coverage to their specific needs and gain more control over their risk management strategies.
The 831(b) tax code, established by the IRS, provides certain advantages for small captive insurance companies. Under this tax code, captives that meet the requirements can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, rather than their underwriting profits. This can lead to significant tax savings for businesses utilizing captive insurance as a risk management tool.
A microcaptive, often referred to as a small captive, is a specific type of captive insurance company that falls within the criteria outlined by the IRS under section 831(b). These microcaptives can be an attractive option for small and mid-sized businesses, as they offer potential tax benefits while providing tailored insurance coverage.
In conclusion, captive insurance, especially microcaptives operating under the IRS 831(b) tax code, can provide businesses with greater flexibility, control, and potential tax advantages. By understanding and leveraging the benefits of captive insurance, companies can enhance their risk management strategies and secure their financial future.
Benefits of the 831(b) Tax Code
The 831(b) tax code offers a range of benefits for businesses considering captive insurance solutions. One significant advantage is the ability to create a tax-efficient structure for managing risks. By establishing a captive insurance company under 831(b), businesses gain more control over their insurance coverage while potentially reducing their overall insurance costs.
Under the 831(b) tax code, captive insurance companies can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, rather than on their entire premium income. This favorable tax treatment allows businesses to accumulate earnings within the captive, creating a potential source of funding for future claims or business expansions. It also offers the opportunity for tax deferral, as the insurance premiums received by the captive can be taxed at a lower rate than if they were received by a traditional insurance company.
Additionally, the 831(b) tax code provides flexibility in choosing the level of insurance coverage needed. By customizing their captive insurance program, businesses can tailor their policies to address specific risks that may be inadequately covered by traditional insurance markets. This enables companies to take a proactive approach to risk management, ensuring they have appropriate coverage and reducing their reliance on external insurers.
In summary, the 831(b) tax code presents businesses with the chance to optimize their risk management strategies. By establishing a captive insurance arrangement and leveraging the benefits offered by this tax code, companies can enhance control over their insurance coverage, potentially reduce costs, and create a valuable financial asset within their organization.
Exploring the Potential of Microcaptives
Microcaptives offer a promising avenue for businesses seeking to optimize their insurance coverage while enjoying significant tax advantages. With the implementation of the IRS 831(b) tax code, the captive insurance landscape has witnessed a shift towards the establishment of small, self-insured entities known as microcaptives. These innovative structures enable businesses to enjoy enhanced risk management capabilities and greater control over their insurance costs.
Operating under the umbrella of the captive insurance framework, microcaptives empower businesses to customize coverage options tailored specifically to their unique risk profiles. By directly assuming a portion of the risk and insuring against it through the microcaptive, businesses can gain increased flexibility in designing insurance programs that align closely with their individual needs. This level of customization can be particularly valuable for those operating in industries with specialized or unique risks that may not be adequately addressed by traditional insurance instruments.

Furthermore, the utilization of the IRS 831(b) tax code allows microcaptives to enjoy attractive tax benefits. Under the code, qualifying microcaptives can elect to pay taxes only on their investment income, rather than the premiums received. This tax advantage enables businesses to accumulate a pool of capital within the microcaptive, fostering a financially robust entity capable of fulfilling its insurance obligations while potentially generating returns on investments. Consequently, microcaptives provide businesses with an effective means of not only managing their risk but also enhancing their overall financial position.
In summary, microcaptives present a compelling proposition for businesses seeking greater control, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in their insurance strategies. Through these autonomous entities, companies can harness the benefits of captive insurance while enjoying the advantages afforded by the IRS 831(b) tax code. By closely examining the potential offered by microcaptives, businesses can explore new avenues to optimize their risk management practices and unlock valuable tax benefits in the process.
Captive insurance, a form of self-insurance, has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses seeking to manage their risks while gaining more control over their insurance programs. This unique concept allows companies to create their own insurance company, known as a captive, to provide coverage for their specific needs. By establishing a captive insurance structure,…